PPT Neoplasms of the Prostate Gland PowerPoint Presentation, free
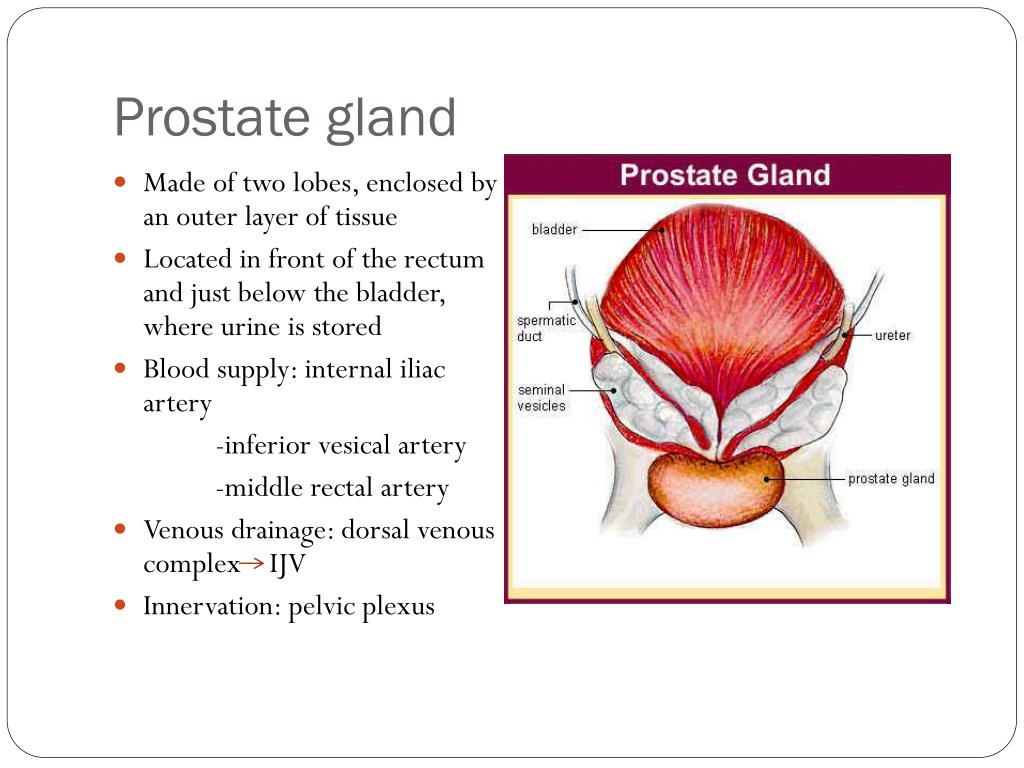
The prostate is a gland below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB). It consists of connective tissues and glandular tissues. It adds fluid to semen, and its muscles help push semen through your urethra. Conditions that affect your prostate include cancer, prostatitis and benign prostatic.
prostateglandslidelabelledhistology SchoolWorkHelper
1 /20. An enlarged prostate occurs when men's prostate gland slowly grows bigger as they age. More than half of men over age 60 have this condition, also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH.

What Is the Prostate Gland? University Health News
Slide 61 Prostate gland with both distended and infolded epithelial linings of the secretory portions. The saccular secretory tubules lie in a dense connective tissue framework (stained pink here). The prostate, along with the seminal vesicles and bulbo-urethral glands, contributes nourishing and lubricating fluids to the ejaculated semen. Slide 62

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
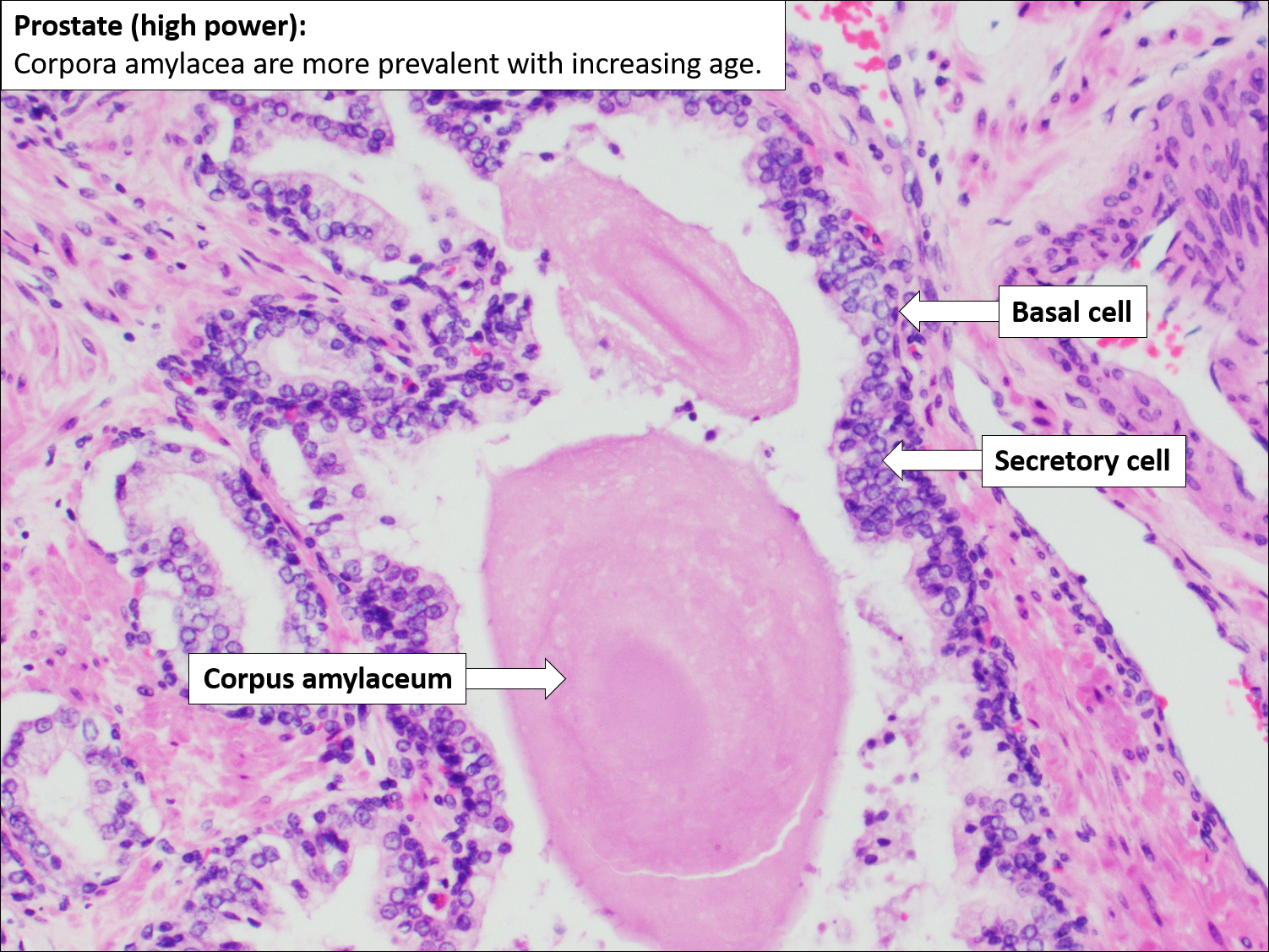
The prostate is a walnut-sized conglomeration of tubulo-acinar glands that surrounds the initial segment of the urethra. This gland produces a secretory product containing citric acid and proteolytic enzymes that prevent coagulation of semen. The prostate often contains prostatic concretions in the acinar lumina.

Pin on норма гист
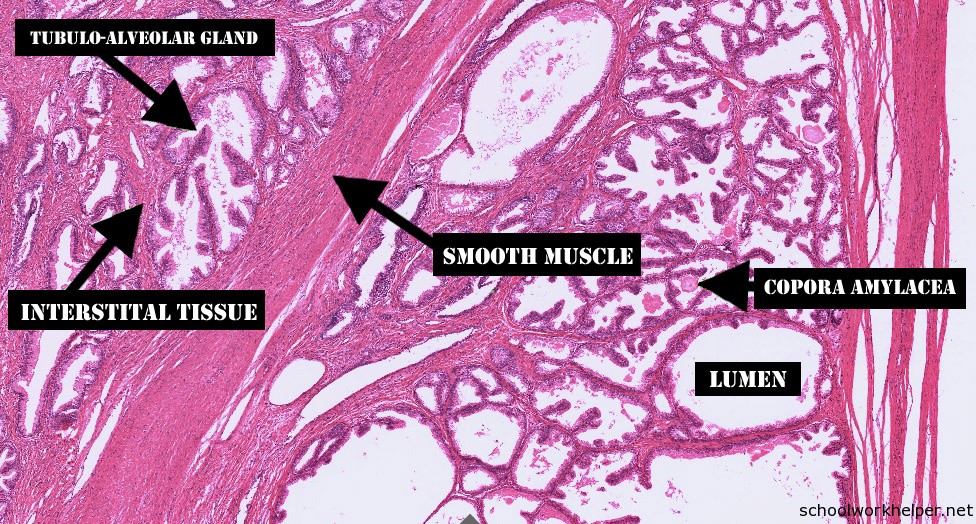
Slide List. Prostate Gland. Prostate Gland The prostate is a set of tubulo-alveolar glands with lumina lined by an epithelium of variable height. The gland contains a stroma containing connective tissue and smooth muscle. The prostate produces a fluid rich in citric acid and proteolytic enzymes that nourish and prevent the coagulation of sperm.
Human Prostate Gland Histology
The Prostate Gland. The prostate is the largest accessory gland in the male reproductive system. It secretes proteolytic enzymes into the semen, which act to break down clotting factors in the ejaculate. This allows the semen to remain in a fluid state, moving throughout the female reproductive tract for potential fertilisation.

Human Prostate Gland Older, sec. 7 µm, H&E Microscope Slide
The prostate in an adult is about the size and shape of a chestnut and contains 15-30 tubuloalveolar glands that empty separately into the prostatic urethra. The most important structures to see on the slide are the prostatic glands that are present over most of the section.

Figure 1.2 from Automatic pathology of prostate cancer in whole mount
It is infection, suppuration and pus formation in the prostate gland. Presentation is fever, rigors, perineal pain, urinary disturbances, and tender Soft fluctuant swelling in the prostate onrectal examination. Often presentation may be retention of urine. Total count will be increased. Urine will show pus cells. US is diagnostic. US is often.

An enlarged prostate gland and incontinence Harvard Health
Use this slide to examine the tubuloalveolar structure of the prostate glands, the smooth muscle between the glands, and at the concretions that are commonly seen within these glands. Webslide UMich 286: Glans penis, human, H&E [DigitalScope] Note the following: 1. Urethra with both stratified squamous and transitional epithelium present. 2.

Prostate Gland Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Stage 1 Stock Illustration
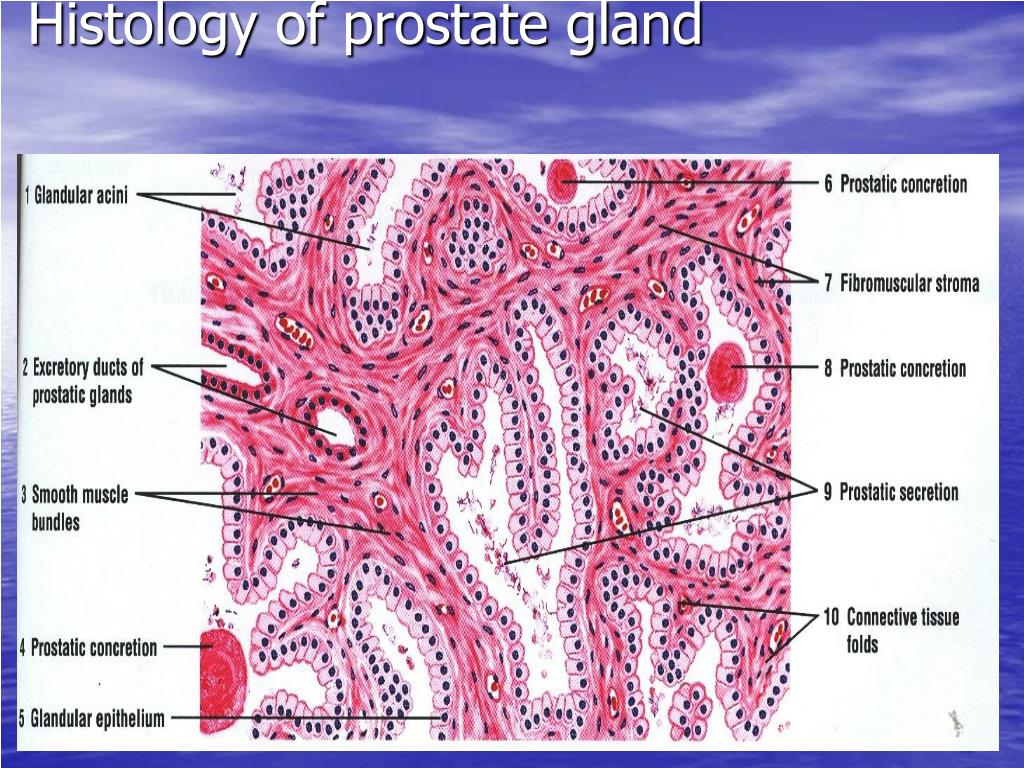
Prostate. The single prostate gland, lying beneath the urinary bladder, is composed of 30-50 individual glands whose secretions empty into the prostatic urethra. The prostate is surrounded by a fibromuscular capsule; the connective tissue around individual glands is also rich in smooth muscle. Ejaculatory ducts pass through the prostate to join.

Prostate Gland, Older, Human, Thin, Micrscope Slide
Slide 24: Picture of Carcinomous prostate glands. Notes: Desmoplastic stroma is thickened stroma that is responsible for the hardness of the prostate; Carcinomous glands have a single layer of cells with large nucleoli. Remember, normal prostate glands have a double-layered epithelium, the basal layer being very flattened, seemingly inactive cells.

1pcs normal human prostate gland section prepared slides, 7 µm sec., H
Publish your next manuscript open access with the Journal of Food Biochemistry. CiteScore: 6.000; JCI: 0.66 and Journal Impact Factor™: 4.0 - Submit Your Research
PPT Histology of the Male Reproductive System (Repro 5) PowerPoint
The prostate gland is a conglomerate of tubular or saclike glands that secrete fluids into the urethra and ejaculatory ducts. The secretory ducts and glands are lined with a moist, folded mucous membrane. The folds permit the tissue to expand while storing fluids. Beneath this layer is connective tissue composed of a thick network of elastic.

normal prostate histology Histology slides, Branches of biology, Prostate
5. •The prostate (prostate gland) is partly glandular and partly fibromuscular -Glandular tissue (1/2) -Involuntary (smooth) muscle (1/4) -Fibrous tissue (1/4) 14. Size & shape • It resembles the size and shape of a chestnut which lies below the bladder and above urogenital diaphragm & surrounds 1st part of urethra.

Prostate Cancer Stages University Health News
Transition zone: 5% of prostatic volume. 2 pear shaped lobes surrounding proximal urethra. Expands after age 50, causing nodular prostatic hyperplasia; may expand to 95% of gland ( Urology 2017;105:136 ) Site of 10% of prostate cancer. Contains moderately compact fascicles of smooth muscle. Central zone: 25% of prostatic volume.

. Histology Slide Download.
Slide 281lex prostate Masson View Virtual Slide. Slide 282 prostate senile H&E View Virtual Slide. The prostate in an adult man is about the size and shape of a chestnut and contains 15-30 tubuloalveolar glands that empty separately into the prostatic urethra. The most important structures to see on the slide are the prostatic glands that are.