[Solved] Solve the triangle B=___° b=____ c=____. C 730 a = 10 490 A B C Course Hero
The perimeter of a triangle is equal to the sum of all the sides of the triangle, and the formula is expressed as, Perimeter of a triangle formula, P = (a + b + c), where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are the three sides of the triangle. The equilateral triangle formula for perimeter is, Perimeter of equilateral triangle = (a +a + a) = 3a.

Example 6 In an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC Examples
Triangle A″B″C″ is formed by a reflection over x = −3 and dilation by a scale factor of 3 from the origin. Which equation shows the correct relationship between ΔABC and ΔA″B″C′? Line segment AB/ Line segment A"B" = 1/3. Square T was translated by the rule (x + 2, y + 2) and then dilated from the origin by a scale factor of 3 to.
Can an equilateral triangle also be isosceles? Socratic
Angle C A B is a right angle. Angle A B C is 30 degrees and angle B C A is 60 degrees. The length of A C is 9 and the length of hypotenuse C B is 18. Which trigonometric ratios are correct for triangle ABC?

Question Video Finding the Measure of an Angle in a Triangle Using the Relations between the
Perimeter of Triangle formula = a + b + c Area of a Triangle

Grade 8 Math Unit 2 Section B Lesson 6 Student Edition
Step 1: Enter the values of any two angles and any one side of a triangle below which you want to solve for remaining angle and sides. Triangle calculator finds the values of remaining sides and angles by using Sine Law. Sine law states that a sinA = b sinB = c sinC a sin A = b sin B = c sin C Cosine law states that-

A triangle ABC with vertices A( 1,0), B( 2,3/4), and C( 1,2) has its orthocentre H . Then
Angle bisector theorem Solve triangles: angle bisector theorem Google Classroom You might need: Calculator ∠ D A C = ∠ B A D . What is the length of C D ― ? Round to one decimal place. A D B θ 8.1 2.8 C θ ? 5.9 Show Calculator Stuck? Review related articles/videos or use a hint. Report a problem Do 4 problems

geometry In the triangle ABC, D and E are points of trisection of segment AB; F is the
In triangle ABC, ∠ C = 90 ∘. If inradius = r and circumradius = R, then find 2(r + R)?(a,b,c are the sides of the triangle opposite to angles A,B and C respectively) View Solution
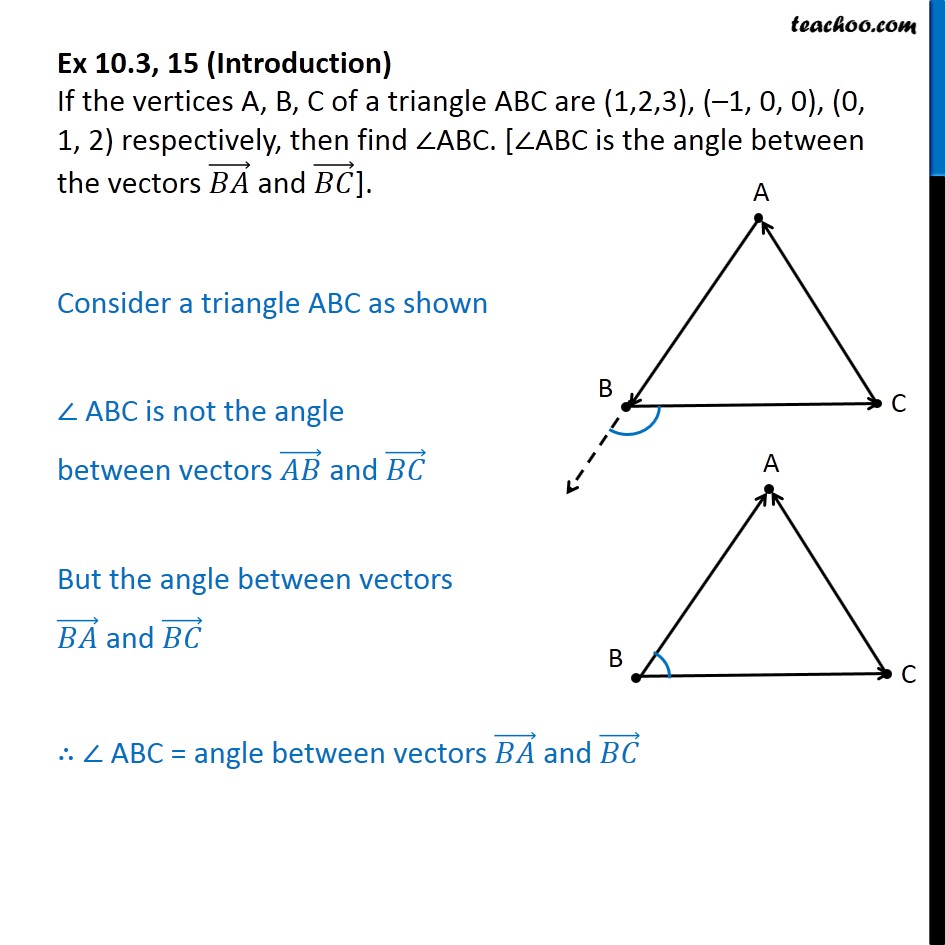
Ex 10.3, 15 If vertices A, B, C of triangle ABC are (1, 2, 3)
C M E ― Why are these words important? We're about to learn the trigonometric functions—sine, cosine, and tangent—which are defined using the words hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent.
"Triangle B, No. 1" by Walter Stomps, Jr Caza Sikes Art Fine Art Appraisers
For similar triangles A B C and X Y Z shown below: X Y = k ( A B) Y Z = k ( B C) X Z = k ( A C) X Y A B = Y Z B C = X Z A C = k. A B C X Y Z. To calculate a missing side length, we: Write a proportional relationship using two pairs of corresponding sides. Plug in known side lengths. We need to know 3.

Which of the following is an obtuse triangle? A. Triangle B B. Triangle A C. Triangle D D
sin (A) < a/c, there are two possible triangles. solve for the 2 possible values of the 3rd side b = c*cos (A) ± √ [ a 2 - c 2 sin 2 (A) ] [1] for each set of solutions, use The Law of Cosines to solve for each of the other two angles. present 2 full solutions. Example: sin (A) = a/c, there is one possible triangle.
SOLVEDAnswer each question and justify your response using a diagram, but do not solve. Given A
A=25 C=80 b=22 A=35 C=26 a=10 a=3 C=90 c=5. how to enter right-angled triangle. a=3 β=25 γ=45. triangle calc if we know the side and two angles. a=3 β=25 T=12. triangle calc, if know side, angle, and area of a triangle. T=2.5 c=2 b=4. find side a if we know sides b, c, and the area of triangle T.

Internal bisector of A of triangle ABC meets side BC at D. A line drawn through D perpendicular
Angles Add to 180°: A + B + C = 180°. When you know two angles you can find the third. 2. Law of Sines (the Sine Rule): a sin (A) = b sin (B) = c sin (C) When there is an angle opposite a side, this equation comes to the rescue. Note: angle A is opposite side a, B is opposite b, and C is opposite c. 3.

Ex 11.2, 6 Let ABC be a right triangle AB = 6 cm, BC = 8 cm, B = 90
Given two sides If you know two other sides of the right triangle, it's the easiest option; all you need to do is apply the Pythagorean theorem: a² + b² = c² If leg a is the missing side, then transform the equation to the form where a is on one side and take a square root: a = √ (c² - b²) If leg b is unknown, then: b = √ (c² - a²)

A triangle has vertices at B(3,0), C(2, 1), D(1,2). Which transformation would produce an
Where a and b are two sides of a triangle, and c is the hypotenuse, the Pythagorean theorem can be written as: a 2 + b 2 = c 2. EX: Given a = 3, c = 5, find b: 3 2 + b 2 = 5 2 9 + b 2 = 25 b 2 = 16 b = 4. Law of sines: the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. Using the law of sines makes it.
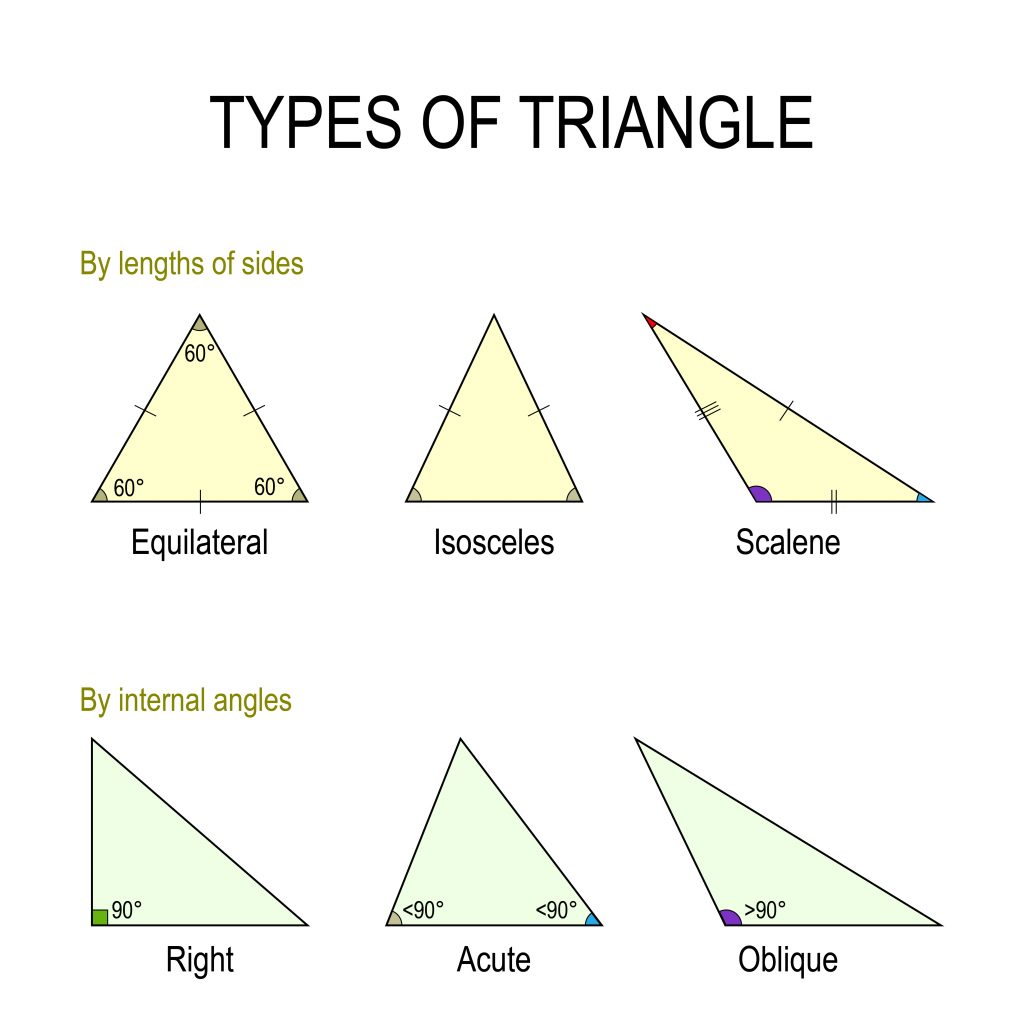
Types & Formulas [Video & Practice] 04/2023
The Law of Sines. The Law of Sines (or Sine Rule) is very useful for solving triangles: a sin A = b sin B = c sin C. It works for any triangle: a, b and c are sides. A, B and C are angles. (Side a faces angle A, side b faces angle B and. side c faces angle C).
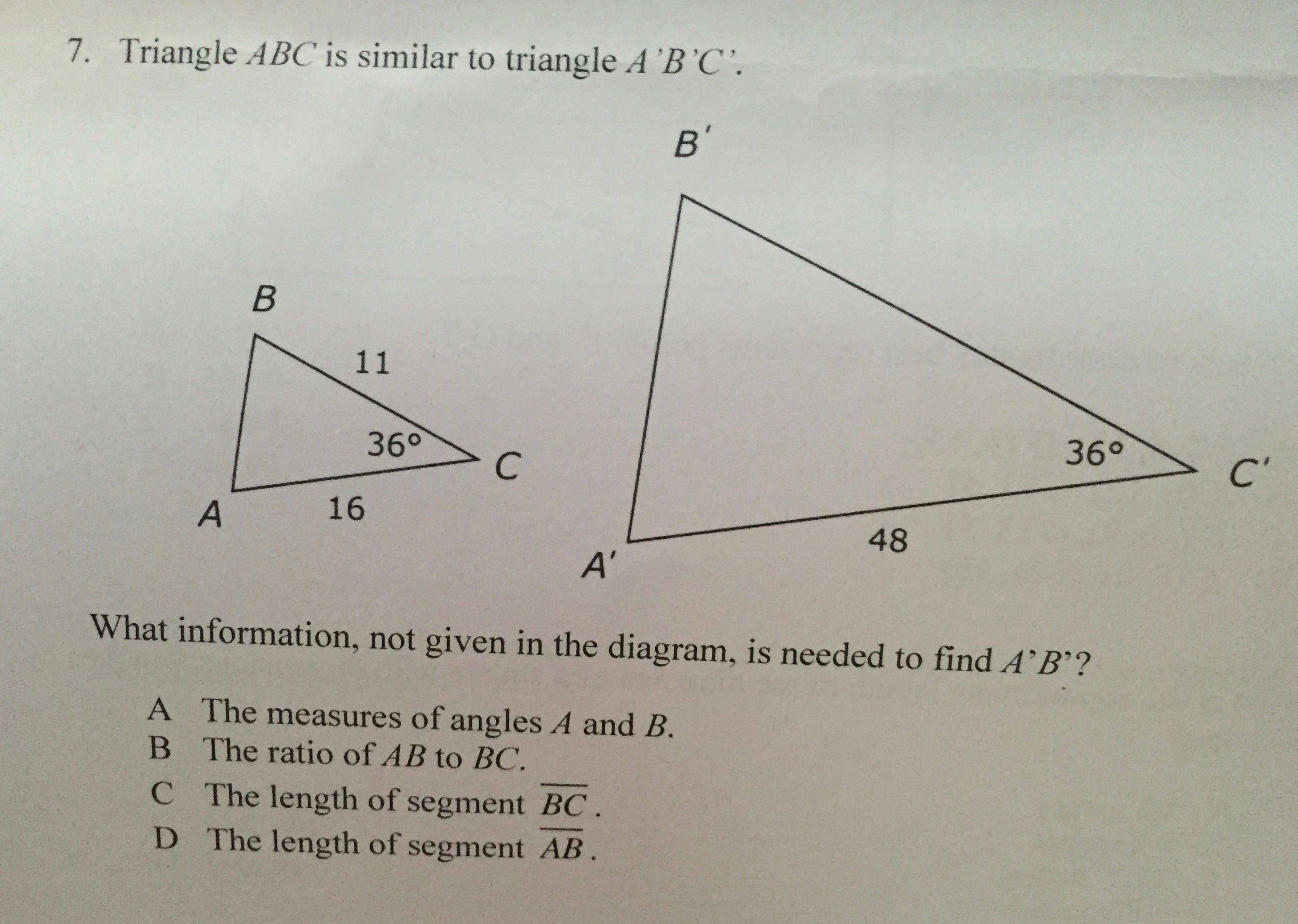
Solved Triangle ABC is similar to triangle A' B' C'. What
Calculator Use A right triangle is a special case of a triangle where 1 angle is equal to 90 degrees. In the case of a right triangle a 2 + b 2 = c 2. This formula is known as the Pythagorean Theorem. In our calculations for a right triangle we only consider 2 known sides to calculate the other 7 unknowns.